IPBrick - Mail Server Configuration
*** Page under construction ***
In this page we present some suggestions to optimize email service functioning in IPBrick installations.
Contents
Improvements
Improvements performed with these configurations:
- General settings – fine adjustment of advanced settings of the email service
- Mail submission – mail submission service for end users, SMTP service for users/clients in ports 587, 465 and 2525
- IMAP proxy – proxy service of IMAP connections, which improves performance of clients' connections and forwarding between several servers
- AutoConfig, AutoDiscover – auto-configuration support service of email clients
Scenarios
These are adjusted accordingly to the standard scenarios, namely:
- Scenario 1 – single server – stand-alone – a single IPBrick.IC server, which will serve the accesses through LAN and/or internet
- Scenario 2 – Multi-server – several servers scenario, considering an IPBrick.I, where the email boxes are lodged, and an IPBrick.C, which will work as a front-end mail-relay, anti-virus and anti-spam for the internet
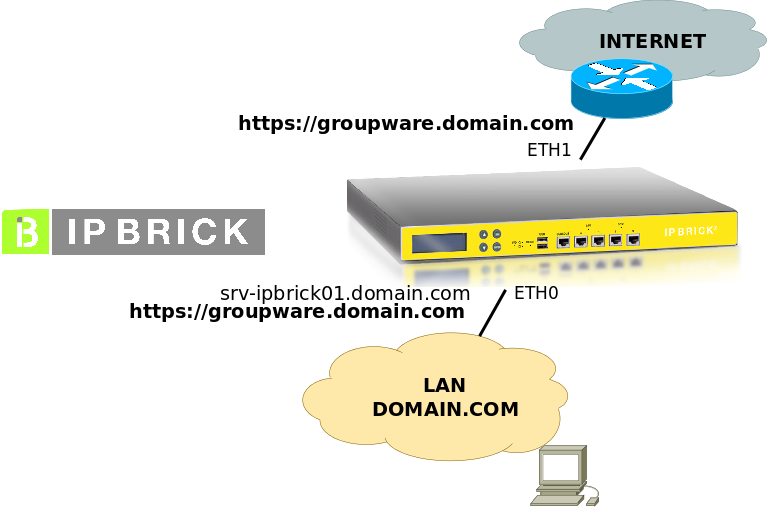
Scenario 1 – Single Server
Network diagram with a single server:
Ahead, we assume that IP network settings are:
- LAN IP (eth0): 192.168.69.199 (/24)
- Internet IP (eth1): 10.0.0.253 (/24)
- in the LAN, the DNS server is secured by this server (srv-ipbrick01)
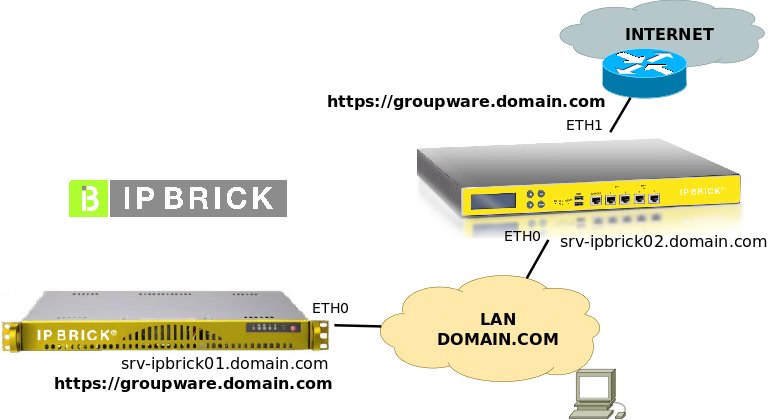
Scenario 2 – Multi-server
Network diagram with several servers; for this exercise we assume two machines:
Ahead, we assume that IP configuration data are:
- srv-ipbrick01.domain.com
- LAN IP (eth0): 192.168.69.1 (/24)
- srv-ipbrick02.domain.com
- LAN IP (eth0): 192.168.69.254 (/24)
- Internet IP (eth1): 10.0.0.253 (/24)
- in the LAN, the DNS server is secured by server srv-ipbrick01
NOTE: In this scenario, the communications server srv-ipbrick02 is configured as IPBRICK.CLIENTE of MASTER srv-ipbrick01.
General Settings
Overall review of mail settings – lets analyse/review each setting and redefine the values according to the scenario. Presentation as provided by IPBrick's menu.
IPBrick.C – Email – Configuration
- Locally delivered domains – here it's necessary to refer the mail domains served by the organization, in this case “domain.com”, e the server itself (FQDN of the server, srv-ipbrick01.domain.com, and srv-ipbrick02.domain.com)
- Authorized domains for relay – refer the same domains that were mentioned in the previous item (locally delivered)
- Authorized networks for relay – adjust to get only and solely the IPs (/32) of the own servers; the users will connect to the intranet server to send will authentication, for example:
- Scenario 1 – single server
- 192.168.69.199 / 32 – Authorized without authentication
- Other networks – Authorized with TLS authentication
- Scenario 2 – Multi-server
- srv-ipbrick01
- 192.168.69.1 / 32 - Authorized without authentication
- Other networks – Authorized with TLS authentication
- srv-ipbrick02
- 192.168.69.1 / 32 - Authorized without authentication
- 192.168.69.254 / 32 - Authorized without authentication
- Other networks – Unauthorized
- srv-ipbrick01
- Scenario 1 – single server
- SMTP routes – usually IPBrick server is prepared to send emails directly to the internet without having to use a relay server; however, in certain configurations, it may be necessary – in these scenarios we assume that we can send directly to the internet, and the configuration recommended here is:
- Scenario 1 – without SMTP routes defined
- Scenario 2 - srv-ipbrick02 (communications) has no defined routes, only srv-ipbrick01 has one route, namely:
- Domain: this field stays empty (it represents all domains)
- Server: srv-ipbrick02.domain.com
IPBrick.C – Email – Configure: Definitions
- Maximum size of a message – by default, it is unlimited, but we will define an example of message limit of 30 MB for attachments
- converter to bytes and adjust to base64 encoding (add 30%): 30 [MB] * 1024 [KB]
- 1024 [bytes] * 1,3 = 40894464 bytes
- Maximum waiting time in a queue – by default, 7 days (604800s); lets define it for 14400s (4h)